Food Entrepreneur
Food Entrepreneur

Seaweed For Humanity begins with the journey of a seaweed boy from Nova Scotia, Canada, to Indonesia after traveling to Hawaii, Japan, Korea, China, India, Tanzania, Philippines, and Malaysia. After graduating as a marine biologist, the seaweed boy worked for various global seaweed processing companies since 1965. The boy’s name is Dr. Iain Charles Neish, and he was appointed president of the International Seaweed Association from 2010 to 2013.
Dr. Iain Charles Neish has dreamed of growing seaweed and living in a tropical country since 1974. It’s not just for his prosperity; seaweed has high value for humanity. Seaweed creates job opportunities and sources of income for vulnerable coastal communities, especially women. Most women don’t have access to and control of coastal natural resources, nor do they have access to the finances, information, or technology for developing and scaling up the seaweed business.
We hope to answer the question: How do we support vulnerable coastal communities and women with seaweed aquaculture? “Seaweed for Humanity” will share the story, which covers the opportunity and challenges of women’s roles and responsibilities in the seaweed value chain and industry of South Sulawesi, Bali, and Nusa Tenggara Timur (NTT).
It’s challenging to introduce seaweed farming to vulnerable coastal communities living in remote areas of Indonesia. Changing daily activities from fishing to farming is difficult. Dr. Neish says it’s not easy to grow seaweed if there is no strong relationship with the local people to address the basic needs of the vulnerable coastal community. However, many are interested in growing seaweed if they can reap the economic benefits.
Seaweed will not grow in a day; therefore, you cannot harvest and sell the product immediately. Unlike fishing, where you can catch and sell for a profit all in a day, seaweed farming takes weeks. But how long can vulnerable coastal communities last without a profit, waiting to get money from cultivating seaweed? Who will give them the loans or capital needed for farming seaweed? Who will buy the seaweed in remote areas? These questions should be addressed before starting to grow seaweed in coastal communities.
Seaweed is what’s called a cash crop. It needs 45 days for growing, harvesting, drying, and selling. Most buyers will go to the main production areas to source dried seaweed through local collectors. Thankfully, seaweed’s demand has grown an average of 10% yearly over the past two years. The buyers can provide down payments to farmers and local collectors to secure their supply. It’s a good job opportunity for the coastal community.
It’s challenging to introduce seaweed farming to vulnerable coastal communities living in remote areas of Indonesia. Changing daily activities from fishing to farming is difficult. Dr. Neish says it’s not easy to grow seaweed if there is no strong relationship with the local people to address the basic needs of the vulnerable coastal community. However, many are interested in growing seaweed if they can reap the economic benefits.
Seaweed will not grow in a day; therefore, you cannot harvest and sell the product immediately. Unlike fishing, where you can catch and sell for a profit all in a day, seaweed farming takes weeks. But how long can vulnerable coastal communities last without a profit, waiting to get money from cultivating seaweed? Who will give them the loans or capital needed for farming seaweed? Who will buy the seaweed in remote areas? These questions should be addressed before starting to grow seaweed in coastal communities.
Seaweed is what’s called a cash crop. It needs 45 days for growing, harvesting, drying, and selling. Most buyers will go to the main production areas to source dried seaweed through local collectors. Thankfully, seaweed’s demand has grown an average of 10% yearly over the past two years. The buyers can provide down payments to farmers and local collectors to secure their supply. It’s a good job opportunity for the coastal community.
Dr. Neish has been working with local communities and living in remote areas to build strong relationships with the vulnerable coastal communities. He is passionate about developing and growing seaweed as an alternative livelihood for these communities, especially women.
The coastal communities should not be left behind and live under poverty lines. They should have good jobs and generate income from coastal natural resources such as fish, lobster, crab, abalone, and seaweed. Dr. Neish introduced seaweed to the coastal communities and transferred his expertise to the local people. He has worked with Haji Adam Omar and Saadah to develop seaweed in the Philippines and then moved to Malaysia and Indonesia. He worked with Made Simbik in Bali and introduced seaweed to coastal communities in Nusa Penida.
Bali was formally the main seaweed production area before the booming tourist industry. Most seaweed farmers had shifted careers to work in hotels, villas, resorts, restaurants, and cafés in Nusa Penida and seaweed production dropped. Many investors were more interested in building infrastructure for the tourist industry than for the seaweed businesses. Thousands of hotels, villas, resorts, restaurants, and cafés have been built in the last two decades in Bali. As a consequence, the seaweed farm was depleted in Nusa Penida, Ceningan, and Lembongan. However, it recovered during the Covid-19 pandemic. Many people lost their jobs in the tourism industry and returned to the sea to grow seaweed. Many coastal communities are now actively growing seaweed as an alternative livelihood for generating income.
Seaweed farming is a family business. The family unit–husband, wife, and children–work together with support from their extended family members. They prepare the input materials and tie seaweed in their home. Working from home creates jobs not only for immediate family members but also for neighbors, allowing them to tie long lines and, in turn, grow more seaweed.
Vulnerable coastal communities, especially women, have an opportunity to work in the seaweed sector. It’s not only tying the seaweed; they also have an option for access and control of coastal resources, such as seaweed farm management and making value-added healthy food and drinks from seaweed. Women have an essential role in developing the seaweed sector in Indonesia. They prepare most input materials, tie seaweed, harvest seaweed, handle the post-harvest process, and trade raw dried seaweeds. They also visit the farm to install and maintain the seaweed during the low tide.
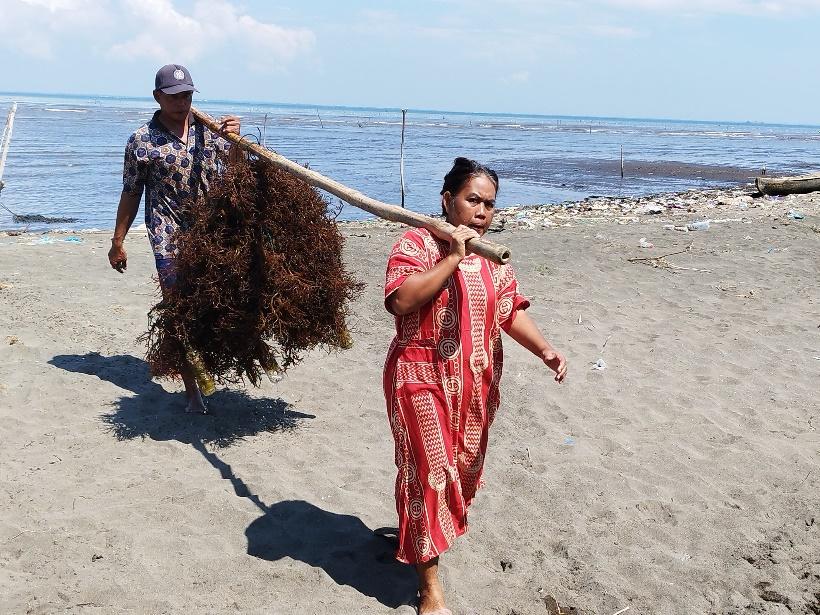

Indonesia has become the second-largest seaweed producer after China and the largest producer of tropical seaweed in the world. Women have a significant role in developing seaweed aquaculture in Indonesia, especially in the primary production areas in South Sulawesi, Bali, and Nusa Tenggara Timur (NTT). It’s fascinating to look at the role of women in developing seaweed aquaculture in Indonesia. Their role is not only in the downstream or farming activities, but they also actively participate in seaweed trading and processing to create business and job opportunities, especially for vulnerable coastal communities.
Patriarchal views of coastal communities at one time limited women from taking the primary role in seaweed aquaculture. It happened in the coastal communities of South Sulawesi, Bali, and Nusa Tenggara Timur.
Formerly, most women were only allowed to prepare input materials, securing seaweed in nylon lines and drying seaweeds. This was due to the supremacy of the father or male who has absolute authority over the family group. Women could not manage seaweed farms, and had limited access and control over coastal natural resources. Most of the seaweed trade is still dominated by men, making it challenging for women to have their own seaweed farms or take hold of business opportunities in the industry.
The value of seaweed, especially cottonii (Eucheuma) and sacol (Kappapychus Striatum), has increased due to the high demand for processed seaweed or carrageenan as an ingredient for food, feed, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. This increased demand has a high potential for creating a positive impact in coastal communities. As such, International development agencies, non-government organizations, and multilateral organizations (such as IFC, World Bank, FAO, ILO, UNIDO, GTZ) have become interested in developing seaweed projects in Eastern Indonesia. These projects would support vulnerable coastal communities by building capacity for seaweed farmers, traders, and processors. The projects aim to address gender equality and support women attempting to access and control coastal natural resources, enhancing their lives as leaders in the industry. With support from these projects and collaboration with multi-stakeholders, Indonesia has become the biggest tropical seaweed producer since 2008, making Indonesia the second largest after China. According to Queensland University research, the Indonesian seaweed sector creates income for over a million coastal people, especially in Eastern Indonesia.
Women’s role in the seaweed sector has changed over the last two decades. A project of OXFAM called Restoring Coastal Livelihoods facilitated vulnerable women in accessing and controlling coastal natural resources and supported emerging women’s economic groups. Thanks to this initiative, women could manage their own farms and traded dried seaweed at the market.
UNIDO SmartFish is another project that provides support to strengthen the trade capacity of the seaweed sector. The Socialization and Training of Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Farming Seaweeds has been delivered to 2,000 seaweed farmers in South Sulawesi, South East Sulawesi, East Java, and Central Java.
Implemented by partners Jaringan Sumber Daya (JaSuDa) and UNIDO in South Sulawesi, SmartFish finalized the SOP monitoring for farming Kappaphycus spp, Eucheuma spp, and Gracilaria spp. In total, 399 farmers have adopted SOP in Bulukumba, 406 farmers in Janeponto, 353 farmers in Maros and 401 farmers in Pangkep.
Mama Yos is a seaweed cultivator who manages her own farm. When her husband lost his job when the pandemic hit, he came to help her grow Cottonii with the off-bottom method at a farm not far from their house. Mama Yos said, “I had difficulties during the Seroja cyclone, which hit in April 2021. My farm assets were devastated and I lost nylon lines and seaweed biomass. I did not have capital and started seaweed farming from zero. We also had a problem with the governor’s regulation which banned the seaweed shipped out to site NTT, and the price dropped from IDR 40,000 to IDR 30,000 per kg.” Most recently, the farm gate price has climbed back up to IDR 40,000 per kg.
The seaweed farmers of Indonesia have faced many challenges such as epiphyte, ice–ice disease, grazer, flooding, and cyclones with strong winds or waves. It’s affected seaweed biomass loss and reduced the productivity and income of the farmers. Vulnerable coastal communities, especially women, have their primary incomes from seaweed farming and business. Despite the challenges, they receive benefits from seaweed farming that outweigh the risk of damage. It’s not only the economic benefit. They also have time to share stories of their journeys while tying seaweeds to improve their lives.
The SOP for Farming Seaweeds had been adopted by the farmers. They also have the equipment to monitor the farm’s water quality changes. Therefore, they could minimize the failure due to extreme salinity, pH, and temperature.
The vulnerable coastal communities, especially women, have their primary incomes from seaweed farming and business. They receive benefits from seaweed farming. It’s not only the economic benefit. They also have time to share stories of their life while tying seaweeds to improve their lives.
Seaweeds contribute wide-reaching ecosystem services both in the water during grow-out and in their application. Research shows that seaweeds sequester inorganic nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, carbon, etc.) and transform them into organic compounds which are key to avoiding nutrient depletion. Producers can mitigate climate-change impacts through nutrient-uptake management during cultivation, emission reductions related to production and distribution, and species and application choices. The multiple intersections of seaweed and climate change make seaweed aquaculture an important tool for addressing broad concerns of climate change, but also reducing the impact on humans.
Macroalgae, or seaweeds, represent a broad group of eukaryotic photosynthetic marine organisms. Unlike microalgae, they are multicellular classes of algae and possess plant-like structural features that grow to large size (50 cm up to 60 m in length). They are typically composed of a blade or lamina, the stipe, and holdfast for anchoring the entire structure to hard substrates in marine environments. The life cycles of macroalgae are complex and diverse, with different species displaying variations of annual and perennial life histories, combinations of reproductive strategies and alternation of generations.
About
Lexicon of Food is produced by The Lexicon, an international NGO that brings together food companies, government agencies, financial institutions, scientists, entrepreneurs, and food producers from across the globe to tackle some of the most complex challenges facing our food systems.
Team
The Aquaculture Channel was developed by an invitation-only food systems solutions activator created by The Lexicon with support from Food at Google. The activator model fosters unprecedented collaborations between leading food service companies, environmental NGOs, government agencies, and technical experts from across the globe.
This website was built by The Lexicon™, a 501(c)(3) tax-exempt nonprofit organization headquartered in Petaluma, CA.
Check out our Privacy Policy, Cookie Policy, and Terms of Use.
© 2024 – Lexicon of Food™
We have no idea who grows our food, what farming practices they use, the communities they support, or what processing it undergoes before reaching our plates.
As a result, we have no ability to make food purchases that align with our values as individuals, or our missions as companies.
To change that, we’ve asked experts to demystify the complexity of food purchasing so that you can better informed decisions about what you buy.
The Lexicon of Food’s community of experts share their insights and experiences on the complex journey food takes to reach our plates. Their work underscores the need for greater transparency and better informed decision-making in shaping a healthier and more sustainable food system for all.
Professionals at universities and research institutions seeking scholarly articles, data, and resources.
Tools to align investment and grant making strategies with advances in agriculture, food production, and emerging markets.
Professionals seeking information on ingredient sourcing, menu planning, sustainability, and industry trends.
Chefs and food industry professionals seeking inspiration on ingredients and sustainable trends to enhance their work.
Individuals interested in food products, recipes, nutrition, and health-related information for personal or family use.
Individuals producing food, fiber, feed, and other agricultural products that support both local and global food systems.
This online platform is years in the making, featuring the contributions of 1000+ companies and NGOs across a dzen domain areas. To introduce you to their work, we’ve assembled personalized experiences with insights from our community of international experts.
Businesses engaged in food production, processing, and distribution that seek insight from domain experts
Those offering specialized resources and support and guidance in agriculture, food production, and nutrition.
Individuals who engage and educate audience on themes related to agriculture, food production, and nutrition.
Nutritional information for professionals offering informed dietary choices that help others reach their health objectives
Those advocating for greater awareness and stronger action to address climate impacts on agriculture and food security.
Professionals seeking curriculum materials, lesson plans, and learning tools related to food and agriculture.
Over half the world’s agricultural production comes from only three crops. Can we bring greater diversity to our plates?
In the US, four companies control nearly 85% of the beef we consume. Can we develop more regionally-based markets?
How can we develop alternatives to single-use plastics that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly?
Could changing the way we grow our food provide benefits for people and the planet, and even respond to climate change?
Can we meet the growing global demand for protein while reducing our reliance on traditional animal agriculture?
It’s not only important what we eat but what our food comes in. Can we develop tools that identify toxic materials used in food packaging?
Explore The Lexicon’s collection of immersive storytelling experiences featuring insights from our community of international experts.
The Great Protein Shift
Our experts use an engaging interactive approach to break down the technologies used to create these novel proteins.
Lexicon of Impacts
Accelerate positive impacts building a common language for investors, communities and project developers to activate catalytic capital for our planet.
Food-related chronic diseases are the biggest burden on healthcare systems. What would happen if we treated food as medicine?
How can we responsibly manage our ocean fisheries so there’s enough seafood for everyone now and for generations to come?
Mobilizing agronomists, farmers, NGOs, chefs, and food companies in defense of biodiversity in nature, agriculture, and on our plates.
Can governments develop guidelines that shift consumer diets, promote balanced nutrition and reduce the risk of chronic disease?
Will sustainably raising shellfish, finfish, shrimp and algae meet the growing demand for seafood while reducing pressure on wild fisheries?
How can a universal visual language to describe our food systems bridge cultural barriers and increase consumer literacy?
What if making the right food choices could be an effective tool for addressing a range of global challenges?
Let’s start with climate change. While it presents our planet with existential challenges, biodiversity loss, desertification, and water scarcity should be of equal concern—they’re all connected.
Instead of seeking singular solutions, we must develop a holistic approach, one that channel our collective energies and achieve positive impacts where they matter most.
To maximize our collective impact, EBF can help consumers focus on six equally important ecological benefits: air, water, soil, biodiversity, equity, and carbon.
We’ve gathered domain experts from over 1,000 companies and organizations working at the intersection of food, agriculture, conservation, and climate change.
The Lexicon™ is a California-based nonprofit founded in 2009 with a focus on positive solutions for a more sustainable planet.
For the past five years, it has developed an “activator for good ideas” with support from Food at Google. This model gathers domain experts from over 1,000 companies and organizations working at the intersection of food, agriculture, conservation, and climate change.
Together, the community has reached consensus on strategies that respond to challenges across multiple domain areas, including biodiversity, regenerative agriculture, food packaging, aquaculture, and the missing middle in supply chains for meat.
Lexicon of Food is the first public release of that work.
Over half the world’s agricultural production comes from only three crops. Can we bring greater diversity to our plates?
In the US, four companies control nearly 85% of the beef we consume. Can we develop more regionally-based markets?
How can we develop alternatives to single-use plastics that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly?
Could changing the way we grow our food provide benefits for people and the planet, and even respond to climate change?
Can we meet the growing global demand for protein while reducing our reliance on traditional animal agriculture?
It’s not only important what we eat but what our food comes in. Can we develop tools that identify toxic materials used in food packaging?
Explore The Lexicon’s collection of immersive storytelling experiences featuring insights from our community of international experts.
The Great Protein Shift
Our experts use an engaging interactive approach to break down the technologies used to create these novel proteins.
Ten Principles for Regenerative Agriculture
What is regenerative agriculture? We’ve developed a framework to explain the principles, practices, ecological benefits and language of regenerative agriculture, then connected them to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.
Food-related chronic diseases are the biggest burden on healthcare systems. What would happen if we treated food as medicine?
How can we responsibly manage our ocean fisheries so there’s enough seafood for everyone now and for generations to come?
Mobilizing agronomists, farmers, NGOs, chefs, and food companies in defense of biodiversity in nature, agriculture, and on our plates.
Can governments develop guidelines that shift consumer diets, promote balanced nutrition and reduce the risk of chronic disease?
Will sustainably raising shellfish, finfish, shrimp and algae meet the growing demand for seafood while reducing pressure on wild fisheries?
How can a universal visual language to describe our food systems bridge cultural barriers and increase consumer literacy?
This game was designed to raise awareness about the impacts our food choices have on our own health, but also the environment, climate change and the cultures in which we live.
First, you can choose one of the four global regions and pick a character that you want to play.
Each region has distinct cultural, economic, historical, and agricultural capacities to feed itself, and each character faces different challenges, such as varied access to food, higher or lower family income, and food literacy.
As you take your character through their day, select the choices you think they might make given their situation.
At the end of the day you will get a report on the impact of your food choices on five areas: health, healthcare, climate, environment and culture. Take some time to read through them. Now go back and try again. Can you make improvements in all five areas? Did one area score higher, but another score lower?
FOOD CHOICES FOR A HEALTHY PLANET will help you better understand how all these regions and characters’ particularities can influence our food choices, and how our food choices can impact our personal health, national healthcare, environment, climate, and culture. Let’s Play!
The FOOD CHOICES FOR A HEALTHY PLANET game allows users to experience the dramatic connections between food and climate in a unique and engaging way. The venue and the game set-up provides attendees with a fun experience, with a potential to add a new layer of storytelling about this topic.
Starting the game: the pilot version of the game features four country/regions: Each reflects a different way people (and the national dietary guidelines) look at diets: Nordic Countries (sustainability), Brazil (local and whole foods instead of ultra-processed foods); Canada (plant-forward), and Indonesia (developing countries).
Personalizing the game: players begin by choosing a country and then a character who they help in making food choices over the course of one day. Later versions may allow for creating custom avatars.
Making tough food choices: This interactive game for all ages shows how the food choices we make impact our health and the environment, and even contribute to climate change.





What we eat matters: at the end of each game, players learn that every decision they make impacts not only their health, but a national healthcare system, the environment, climate and even culture.
We’d love to know more about you and why you think you will be a great fit for this position! Shoot us an email introducing you and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible!
Providing best water quality conditions to ensure optimal living condition for growth, breeding and other physiological needs
Water quality is sourced from natural seawater with dependency on the tidal system. Water is treated to adjust pH and alkalinity before stocking.
Producers that own and manages the farm operating under small-scale farming model with limited input, investment which leads to low to medium production yield
All 1,149 of our farmers in both regencies are smallholder farmers who operate with low stocking density, traditional ponds, and no use of any other intensification technology.
Safe working conditions — cleanliness, lighting, equipment, paid overtime, hazard safety, etc. — happen when businesses conduct workplace safety audits and invest in the wellbeing of their employees
Company ensure implementation of safe working conditions by applying representative of workers to health and safety and conduct regular health and safety training. The practices are proven by ASIC standards’ implementation
Implementation of farming operations, management and trading that impact positively to community wellbeing and sustainable better way of living
The company works with local stakeholders and local governments to create support for farmers and the farming community in increasing resilience. Our farming community is empowered by local stakeholders continuously to maintain a long generation of farmers.
Freezing seafood rapidly when it is at peak freshness to ensure a higher quality and longer lasting product
Our harvests are immediately frozen with ice flakes in layers in cool boxes. Boxes are equipped with paper records and coding for traceability. We ensure that our harvests are processed with the utmost care at <-18 degrees Celsius.
Sourcing plant based ingredients, like soy, from producers that do not destroy forests to increase their growing area and produce fish feed ingredients
With adjacent locations to mangroves and coastal areas, our farmers and company are committed to no deforestation at any scale. Mangrove rehabilitation and replantation are conducted every year in collaboration with local authorities. Our farms are not established in protected habitats and have not resulted from deforestation activity since the beginning of our establishment.
Implement only natural feeds grown in water for aquatic animal’s feed without use of commercial feed
Our black tiger shrimps are not fed using commercial feed. The system is zero input and depends fully on natural feed grown in the pond. Our farmers use organic fertilizer and probiotics to enhance the water quality.
Enhance biodiversity through integration of nature conservation and food production without negative impact to surrounding ecosysytem
As our practices are natural, organic, and zero input, farms coexist with surrounding biodiversity which increases the volume of polyculture and mangrove coverage area. Farmers’ groups, along with the company, conduct regular benthic assessments, river cleaning, and mangrove planting.
THE TERM “MOONSHOT” IS OFTEN USED TO DESCRIBE an initiative that goes beyond the confines of the present by transforming our greatest aspirations into reality, but the story of a moonshot isn’t that of a single rocket. In fact, the Apollo program that put Neil Armstrong on the moon was actually preceded by the Gemini program, which in a two-year span rapidly put ten rockets into space. This “accelerated” process — with a new mission nearly every 2-3 months — allowed NASA to rapidly iterate, validate their findings and learn from their mistakes. Telemetry. Propulsion. Re-entry. Each mission helped NASA build and test a new piece of the puzzle.
The program also had its fair share of creative challenges, especially at the outset, as the urgency of the task at hand required that the roadmap for getting to the moon be written in parallel with the rapid pace of Gemini missions. Through it all, the NASA teams never lost sight of their ultimate goal, and the teams finally aligned on their shared responsibilities. Within three years of Gemini’s conclusion, a man did walk on the moon.
FACT is a food systems solutions activator that assesses the current food landscape, engages with key influencers, identifies trends, surveys innovative work and creates greater visibility for ideas and practices with the potential to shift key food and agricultural paradigms.
Each activator focuses on a single moonshot; instead of producing white papers, policy briefs or peer-reviewed articles, these teams design and implement blueprints for action. At the end of each activator, their work is released to the public and open-sourced.
As with any rapid iteration process, many of our activators re-assess their initial plans and pivot to address new challenges along the way. Still, one thing has remained constant: their conviction that by working together and pooling their knowledge and resources, they can create a multiplier effect to more rapidly activate change.
Co-Founder
THE LEXICON
Vice President
Global Workplace Programs
GOOGLE
Who can enter and how selections are made.
A Greener Blue is a global call to action that is open to individuals and teams from all over the world. Below is a non-exhaustive list of subjects the initiative targets.
To apply, prospective participants will need to fill out the form on the website, by filling out each part of it. Applications left incomplete or containing information that is not complete enough will receive a low score and have less chance of being admitted to the storytelling lab.
Nonprofit organizations, communities of fishers and fish farmers and companies that are seeking a closer partnership or special support can also apply by contacting hello@thelexicon.org and interacting with the members of our team.
Special attention will be given to the section of the form regarding the stories that the applicants want to tell and the reasons for participating. All proposals for stories regarding small-scale or artisanal fishers or aquaculturists, communities of artisanal fishers or aquaculturists, and workers in different steps of the seafood value chain will be considered.
Stories should show the important role that these figures play in building a more sustainable seafood system. To help with this narrative, the initiative has identified 10 principles that define a more sustainable seafood system. These can be viewed on the initiative’s website and they state:
Seafood is sustainable when:
Proposed stories should show one or more of these principles in practice.
Applications are open from the 28th of June to the 15th of August 2022. There will be 50 selected applicants who will be granted access to The Lexicon’s Total Storytelling Lab. These 50 applicants will be asked to accept and sign a learning agreement and acceptance of participation document with which they agree to respect The Lexicon’s code of conduct.
The first part of the lab will take place online between August the 22nd and August the 26th and focus on training participants on the foundation of storytelling, supporting them to create a production plan, and aligning all of them around a shared vision.
Based on their motivation, quality of the story, geography, and participation in the online Lab, a selected group of participants will be gifted a GoPro camera offered to the program by GoPro For A Change. Participants who are selected to receive the GoPro camera will need to sign an acceptance and usage agreement.
The second part of the Storytelling Lab will consist of a production period in which each participant will be supported in the production of their own story. This period goes from August 26th to October 13th. Each participant will have the opportunity to access special mentorship from an international network of storytellers and seafood experts who will help them build their story. The Lexicon also provides editors, animators, and graphic designers to support participants with more technical skills.
The final deadline to submit the stories is the 14th of October. Participants will be able to both submit complete edited stories, or footage accompanied by a storyboard to be assembled by The Lexicon’s team.
All applicants who will exhibit conduct and behavior that is contrary to The Lexicon’s code of conduct will be automatically disqualified. This includes applicants proposing stories that openly discriminate against a social or ethnic group, advocate for a political group, incite violence against any group, or incite to commit crimes of any kind.
All submissions must be the entrant’s original work. Submissions must not infringe upon the trademark, copyright, moral rights, intellectual rights, or rights of privacy of any entity or person.
Participants will retain the copyrights to their work while also granting access to The Lexicon and the other partners of the initiative to share their contributions as part of A Greener Blue Global Storytelling Initiative.
If a potential selected applicant cannot be reached by the team of the Initiative within three (3) working days, using the contact information provided at the time of entry, or if the communication is returned as undeliverable, that potential participant shall forfeit.
Selected applicants will be granted access to an advanced Storytelling Lab taught and facilitated by Douglas Gayeton, award-winning storyteller and information architect, co-founder of The Lexicon. In this course, participants will learn new techniques that will improve their storytelling skills and be able to better communicate their work with a global audience. This skill includes (but is not limited to) how to build a production plan for a documentary, how to find and interact with subjects, and how to shoot a short documentary.
Twenty of the participants will receive a GoPro Hero 11 Digital Video and Audio Cameras by September 15, 2022. Additional participants may receive GoPro Digital Video and Audio Cameras to be announced at a later date. The recipients will be selected by advisors to the program and will be based on selection criteria (see below) on proposals by Storytelling Lab participants. The selections will keep in accordance with Lab criteria concerning geography, active participation in the Storytelling Lab and commitment to the creation of a story for the Initiative, a GoPro Camera to use to complete the storytelling lab and document their story. These recipients will be asked to sign an acceptance letter with terms of use and condition to receive the camera.
The Lexicon provides video editors, graphic designers, and animators to support the participants to complete their stories.
The submitted stories will be showcased during international and local events, starting from the closing event of the International Year of Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022 in Rome, in January 2023. The authors of the stories will be credited and may be invited to join.
Storytelling lab participation:
Applicants that will be granted access to the storytelling Lab will be evaluated based on the entries they provided in the online form, and in particular:
Applications will be evaluated by a team of 4 judges from The Lexicon, GSSI and the team of IYAFA (Selection committee).
When selecting applications, the call promoters may request additional documentation or interviews both for the purpose of verifying compliance with eligibility requirements and to facilitate proposal evaluation.
Camera recipients:
Participants to the Storytelling Lab who will be given a GoPro camera will be selected based on:
The evaluation will be carried out by a team of 4 judges from The Lexicon, GSSI and the team of IYAFA (Selection committee).
Incidental expenses and all other costs and expenses which are not specifically listed in these Official Rules but which may be associated with the acceptance, receipt and use of the Storytelling Lab and the camera are solely the responsibility of the respective participants and are not covered by The Lexicon or any of the A Greener Blue partners.
All participants who receive a Camera are required to sign an agreement allowing GoPro for a Cause, The Lexicon and GSSI to utilize the films for A Greener Blue and their promotional purposes. All participants will be required to an agreement to upload their footage into the shared drive of The Lexicon and make the stories, films and images available for The Lexicon and the promoting partners of A Greener Blue.